An ECG in Disguise?
September 15, 2024
By Ken Grauer, MD
The electrocardiogram (ECG) in the figure was recorded from an older man following a bradycardic and hypotensive episode. What ECG diagnosis is suggested by this tracing? What are the clinical implications of this diagnosis? Hint: What type of bundle branch block is present?
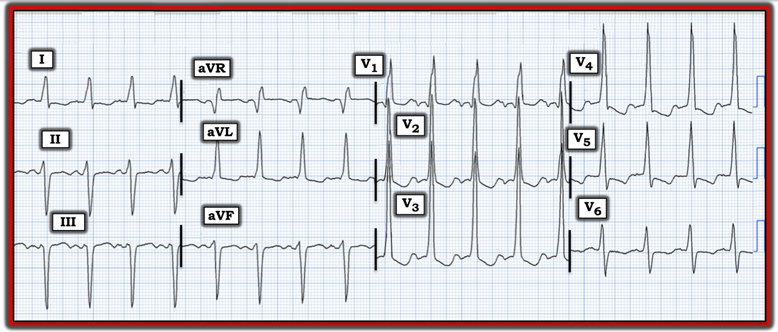
Interpretation: The initial rhythm in today’s tracing is sinus tachycardia at a rate of ~115 beats/minute.
- The QRS complex is wide. QRS morphology in the chest leads is consistent with right bundle branch block (RBBB) — as seen by the predominantly upright (qR) pattern in right-sided lead V1, with a positive R wave and a wide terminal S wave in left-sided lead V6.
- In contrast, the wide QRS seen in the limb leads suggests left bundle branch block (LBBB), given the all upright R wave in lead aVL and the almost all upright R wave in left-sided lead I. The frontal plane axis is decidedly leftward (i.e., with predominantly negative QRS complexes in each of the inferior leads).
- ST-T waves show some flattening and ST-T wave depression that does not look acute and is not unexpected given the pattern of QRS widening.
Impression: The presence of a sinus rhythm with QRS widening, in which QRS morphology resembles RBBB conduction in the chest leads — but LBBB conduction with marked left axis deviation in the limb leads — is consistent with the entity known as “masquerading” bundle branch block (MBBB).
- MBBB is an uncommon clinical entity that identifies patients with severe underlying heart disease and a poor long-term prognosis.
- These patients are at high risk for developing complete AV block — and often require permanent pacing. The bradycardia and hypotensive episode described in the introduction of this case is not surprising.
Note: For more information about this case, visit https://tinyurl.com/KG-Blog-419.